India recently made headlines by surpassing Japan to become the world’s third-largest economy. This achievement, highlighted in reports from institutions such as S&P Global, reflects India’s sustained economic growth and strategic positioning on the global stage. Several key national and international factors have contributed to this rise.
National Factors
- Rapid GDP Growth
India has consistently been one of the fastest-growing major economies, with GDP growth rates above 6% in recent years. In 2023, India saw a remarkable 7.8% growth in the April-June quarter, driven by strong domestic demand and a rebound from the COVID-19 pandemic. The country’s nominal GDP is expected to rise from $3.5 trillion in 2022 to over $7 trillion by 2030. - Demographic Advantage
India’s young and growing population provides it with a labor force unmatched by most economies. The median age in India is 28.4 years, giving the country a significant edge over aging economies like Japan. This demographic dividend is key to sustaining economic growth as the young workforce drives both productivity and consumption. - Digitalization and Technological Innovation
The rise of digital infrastructure has transformed India’s economy. Initiatives like Digital India, and the penetration of 4G and 5G technologies, have led to a boom in sectors like e-commerce, fintech, and IT services. India is now home to a vibrant startup ecosystem, with unicorns in tech, logistics, and other sectors gaining global attention. - Manufacturing and Infrastructure Push
India’s “Make in India” initiative has fueled industrial growth by attracting foreign investment in manufacturing sectors such as electronics, automobiles, and pharmaceuticals. The push for infrastructure development, including roadways, ports, and power projects, has improved the overall ease of doing business and boosted industrial output. - Energy Transition
India’s investment in renewable energy, particularly solar and wind power, positions it as a global leader in the energy transition. This shift towards sustainability has attracted international investments and aligns with global trends in green technology.
International Factors
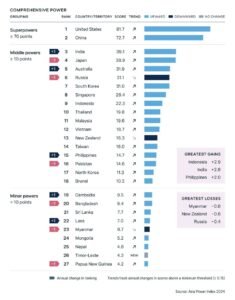
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
India has become a magnet for foreign investments, particularly from technology giants like Google, Microsoft, and Facebook, thanks to its growing consumer base and digital transformation. The country has also seen significant investments in its manufacturing and services sectors, which are central to its GDP growth. - Geopolitical Shifts
As global trade realigns due to geopolitical tensions, India has emerged as a key partner for Western economies looking to diversify supply chains away from China. India’s growing involvement in strategic alliances like the Quad (India, the US, Japan, and Australia) has strengthened its geopolitical influence. - Challenges in Japan and Other Economies
While India has surged ahead, Japan has experienced economic stagnation driven by an aging population, a shrinking labor force, and weak domestic demand. Germany, another close competitor, has also faced challenges, including an industrial slowdown. These conditions have allowed India to leapfrog both economies. - Global Supply Chain Reconfiguration
Global supply chains are shifting as companies seek to reduce their dependency on China. India has benefited from this reconfiguration, with global corporations expanding operations in the country due to its strategic geographic location, skilled labor, and supportive business environment.
Current Implications and Future Outlook
India’s rise as the third-largest economy not only enhances its global stature but also sets the stage for its growing influence in shaping international economic policies. As India’s economy continues to expand, it is expected to surpass Germany by 2030, with projections placing its GDP above $7 trillion. This rise will be supported by technological advancements, digitalization, and sustainable development initiatives.
In conclusion, India’s leap to becoming the third-largest economy is the result of strategic domestic reforms, demographic advantages, digital transformation, and global geopolitical shifts. This ascent underscores India’s growing role as a key player in the global economy and sets the foundation for its continued expansion in the coming decade.







